Move to Point > 2D

Contents
Move to Point
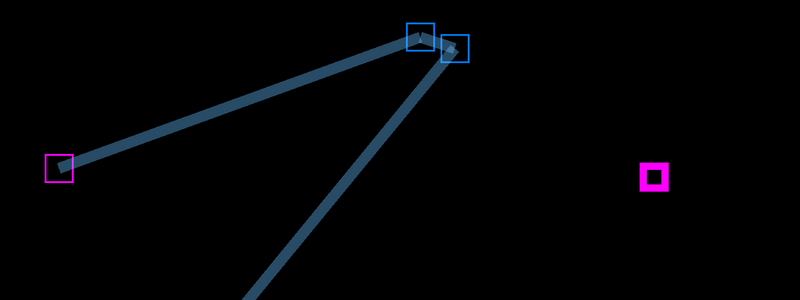
This demonstrates how to move a player (or other object) to a point as determined by clicking on the screen. Left mouse click on the screen and the green circle will move to the point, recalcuting X & Y directions as it moves therefore moving smoothly. Note that this does not take into account collisions with other objects, if you would like to also check for collisions whilst moving then this example includes collision checking. View on Github
Before you start
I am a self taught Go programmer and do it as a hobby, the code below is my own interpretation of how to do something, probably not the only way or the best way. This is intended as a resource to learn some basic Raylib and Go game dev skills. If you want to use any of the code anywhere else, feel free to do so.
Code
package main
import (
"math"
rl "github.com/gen2brain/raylib-go/raylib"
)
/* MORE RAYLIB GO EXAMPLES ARE AVAILABLE HERE:
https://github.com/unklnik/raylib-go-more-examples
*/
var (
scrW, scrH int // SCREEN WIDTH & HEIGHT
player, cnt, clickPoint rl.Vector2 //PLAYER, SCREEN CENTER, MOUSE CLICK VECTOR2
nextPosition rl.Rectangle //COLLISION RECTANGLE FOR MOVE TO POINT
playerSpeed = float32(8) //MAX SPEED PLAYER MOVES
playerDirX, playerDirY float32 //X & Y DIRECTION SPEEDS
)
func main() {
rl.InitWindow(0, 0, "move to point - raylib go - https://github.com/unklnik/raylib-go-more-examples")
scrW, scrH = rl.GetScreenWidth(), rl.GetScreenHeight() // GET SCREEN SIZES
rl.SetWindowState(rl.FlagBorderlessWindowedMode) //SET WINDOW STATE
rl.SetWindowSize(scrW, scrH) // SET WINDOW SIZE
//rl.ToggleFullscreen() // UNCOMMENT IF YOU HAVE DISPLAY ISSUES WITH OVERLAPPING WINDOW BARS
camera := rl.Camera2D{} // DEFINES THE CAMERA
camera.Zoom = 1.0 //SETS CAMERA ZOOM
cnt = rl.NewVector2(float32(scrW/2), float32(scrH/2)) //SCREEN CENTER
player, clickPoint = cnt, cnt //SET INITIAL PLAYER & CLICKPOINT POSITIONS
rl.SetTargetFPS(60) // NUMBER OF FRAMES DRAWN IN A SECOND
for !rl.WindowShouldClose() {
//IF LEFT MOUSE CLICKED CREATE COLLISION RECTANGLE FROM CLICK POINT
if rl.IsMouseButtonPressed(rl.MouseButtonLeft) {
size := float32(16)
clickPoint = rl.GetMousePosition()
nextPosition = rl.NewRectangle(clickPoint.X-size/2, clickPoint.Y-size/2, size, size)
}
//IF CLICK POINT IS NOT CENTER & PLAYER IS NOT COLLIDING WITH NEXT POSITION RECTANGLE MOVE
if clickPoint != cnt && !rl.CheckCollisionPointRec(player, nextPosition) {
player.X += playerDirX //MOVE X DIRECTION
player.Y += playerDirY //MOVE Y DIRECTION
diffX := absdiff(player.X, clickPoint.X) //ABSOLUTE DISTANCE BETWEEN X POINTS
diffY := absdiff(player.Y, clickPoint.Y) //ABSOLUTE DISTANCE BETWEEN Y POINTS
if diffX > diffY { //IF X DISTANCE IS LARGER THAN Y DISTANCE
//DIRECTION X SPEED = PLAYER MAX SPEED
playerDirX = playerSpeed
//DIRECTION Y SPEED = Y DISTANCE DIVIDED BY (X DISTANCE DIVIDED BY MAX SPEED)
playerDirY = diffY / (diffX / playerSpeed)
} else {
playerDirY = playerSpeed
playerDirX = diffX / (diffY / playerSpeed)
}
//CHANGES TO NEGATIVE IF CLICKPOINT X IS LEFT OF PLAYER
if clickPoint.X < player.X {
playerDirX = -playerDirX
}
//CHANGES TO NEGATIVE IF CLICKPOINT Y IS ABOVE PLAYER
if clickPoint.Y < player.Y {
playerDirY = -playerDirY
}
}
rl.BeginDrawing()
rl.ClearBackground(rl.Black)
rl.BeginMode2D(camera)
if clickPoint != cnt {
rl.DrawRectangleLinesEx(nextPosition, 2, rl.Magenta) //DRAW COLLISION RECTANGLE
}
rl.DrawCircleV(player, 32, rl.Fade(rl.Green, 0.4)) //DRAW PLAYER CIRCLE
rl.DrawText("LEFT MOUSE CLICK ON THE SCREEN TO MOVE TO POINT", 10, 10, 20, rl.White)
rl.EndMode2D()
rl.EndDrawing()
}
rl.CloseWindow()
}
// FUNCTION TO CALCULATE ABSOLUTE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO VALUES FOR NEGATIVE VALUES
func absdiff(num1, num2 float32) float32 {
num := float32(0)
if num1 == num2 {
num = 0
} else {
if num1 <= 0 && num2 <= 0 {
num1 = getabs(num1)
num2 = getabs(num2)
if num1 > num2 {
num = num1 - num2
} else {
num = num2 - num1
}
} else if num1 <= 0 && num2 >= 0 {
num = num2 + getabs(num1)
} else if num2 <= 0 && num1 >= 0 {
num = num1 + getabs(num2)
} else if num2 >= 0 && num1 >= 0 {
if num1 > num2 {
num = num1 - num2
} else {
num = num2 - num1
}
}
}
return num
}
// FUNCTION TO CALCULATE ABSOLUTE VALUE FOR NEGATIVE VALUES
func getabs(value float32) float32 {
value2 := float64(value)
value = float32(math.Abs(value2))
return value
}
Video
Want to give it a Go?
To start making games with Go and Raylib you will need:
- Go - https://go.dev/
- TDM-GCC - https://jmeubank.github.io/tdm-gcc/
- Git - https://git-scm.com/downloads
- Go Bindings for Raylib - https://github.com/gen2brain/raylib-go
- Visual Studio Code - https://code.visualstudio.com/
You can, of course, use other code editors however VS Code is my own personal preference